
NET BCL, a large collection of classes that have comprehensive and streamlined features such as powerful XML, Database, Serialization, IO, String, and Networking support, and more. Robust Base Class Library (BCL) – Xamarin applications use the.Modern language constructs – Xamarin applications are written in C#, a modern language that includes significant improvements over Objective-C and Java such as dynamic language features, functional constructs such as lambdas, LINQ, parallel programming, generics, and more.Additionally, Xamarin offers binding projects that allow you to bind native Objective-C and Java libraries using a declarative syntax.

#XAMARIN STUDIO ANDROID#
This functionality lets you use existing iOS and Android libraries written in Objective-C, Java, or C/C++. Objective-C, Java, C, and C++ Interop – Xamarin provides facilities for directly invoking Objective-C, Java, C, and C++ libraries, giving you the power to use a wide array of third party code.Strongly-typed bindings lead to fewer runtime errors and higher-quality applications. Additionally, these bindings are strongly-typed, which means that they’re easy to navigate and use, and provide robust compile-time type checking and during development. Complete binding for the underlying SDKs – Xamarin contains bindings for nearly the entire underlying platform SDKs in both iOS and Android.Xamarin combines the abilities of native platforms, while adding features that include: NET, which automatically handles tasks such as memory allocation, garbage collection and interoperability with underlying platforms.įor more information about platform-specific architecture, see Xamarin.Android and Xamarin.iOS.
#XAMARIN STUDIO CODE#
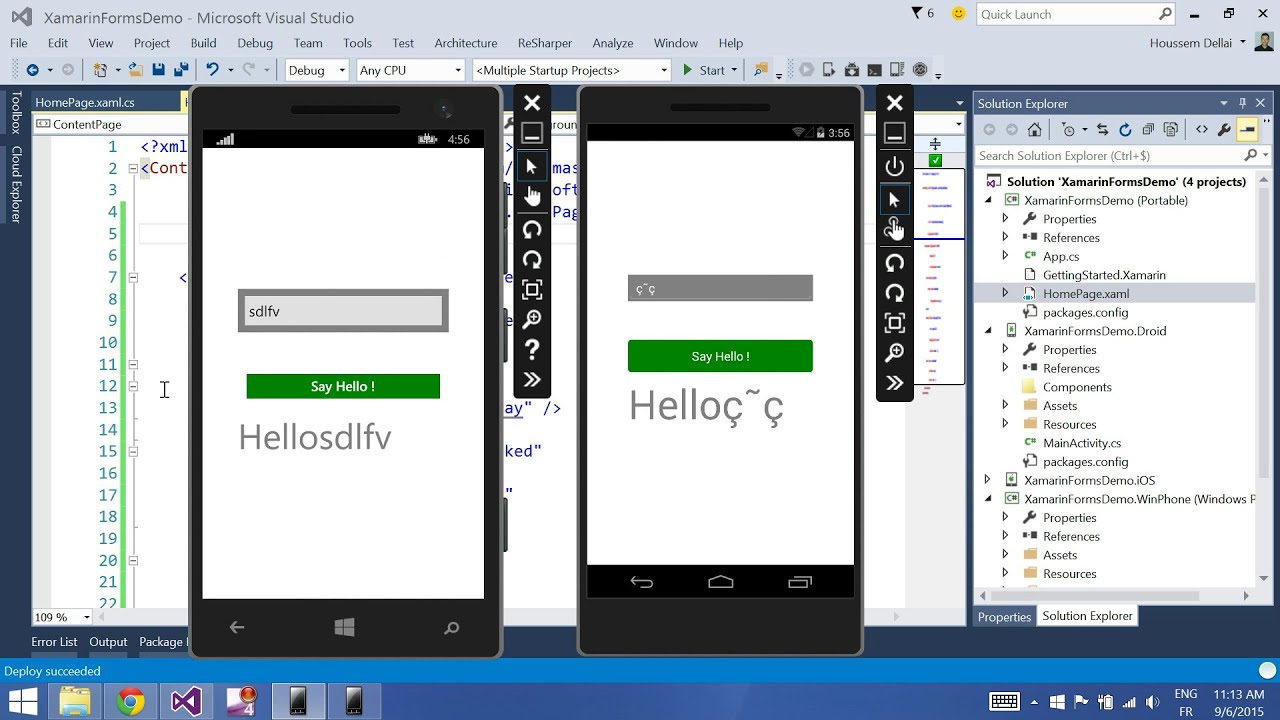
In most cases, 80% of application code is sharable using Xamarin. Xamarin allows you to create native UI on each platform and write business logic in C# that is shared across platforms. The diagram shows the overall architecture of a cross-platform Xamarin application.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
